Prefabricated Homes – Affordable and Efficient Housing Options with Fast Installation
Prefabricated homes represent a revolutionary approach to residential construction, offering homeowners a faster, more cost-effective alternative to traditional building methods. These factory-built structures combine quality craftsmanship with streamlined production processes, delivering complete housing solutions that can be assembled on-site in a fraction of the time required for conventional construction.
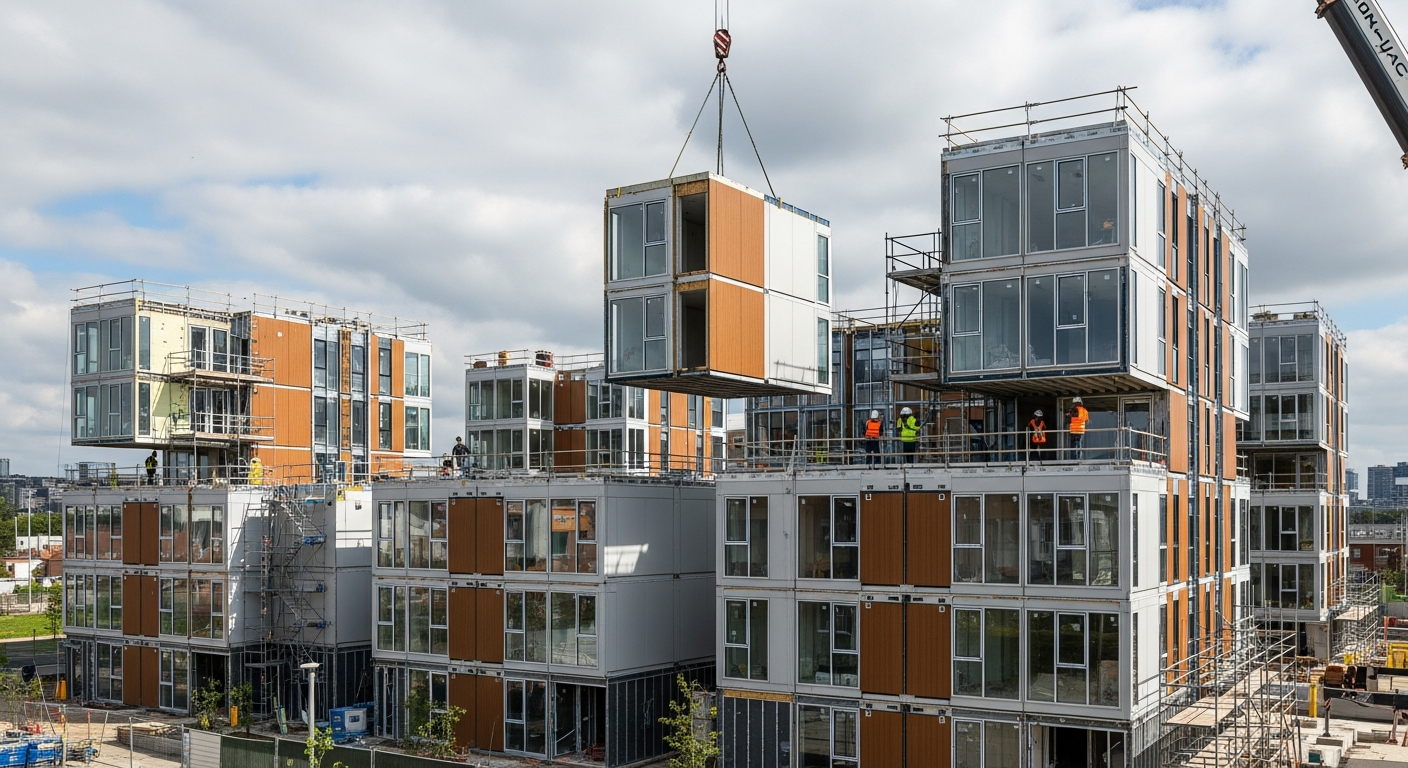

Modern prefabrication combines off-site manufacturing with on-site assembly to deliver homes that are precise, efficient, and comparatively quick to complete. While the approach differs from traditional construction, the result is a permanent residence that can meet or exceed code requirements when properly planned and executed. The sections below explain definitions, methods, design choices, rules to know, and practical pricing insights for buyers in the United States.
What defines prefabricated homes and how they are built?
Prefabricated homes are constructed largely off-site in a controlled factory. Major categories include manufactured homes (built under the federal HUD Code), modular homes (built to the International Residential Code and state modular programs), and panelized systems (factory-built wall, floor, and roof panels assembled on-site). Factories fabricate structural components, integrate mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems, and apply finishes before transport. Modules or panels are trucked to the property, a crane sets them on a prepared foundation, and licensed trades complete connections, weather sealing, and final inspections.
How do they compare with traditional building methods?
Compared with fully site-built projects, prefab offers parallel workflows: foundation work occurs on-site while the home is fabricated in the factory, compressing schedules and reducing weather delays. Precision jigs and repeatable processes improve quality consistency and can reduce material waste. Predictable factory labor may lower risk of cost overruns. Limitations include transport dimensions, crane access, and certain custom geometries that are easier with on-site builds. Performance is comparable or better when modules are engineered for local wind, seismic, and energy requirements, and when air sealing is completed carefully during installation.
What designs and customization options are available?
Design paths typically range from catalog plans with finish packages to semi-custom layouts and fully custom modular builds. Options include accessory dwelling units, single-story ranch plans, multi-story homes, and townhome-scale configurations. Exterior choices often include fiber-cement or wood siding, stucco, and metal cladding, while interiors can be specified with different cabinetry, countertops, flooring, and fixtures. Many providers offer upgrade bundles such as enhanced insulation, high-efficiency windows, heat pumps, solar-ready electrical, and smart-home integrations. Universal design elements—like zero-threshold entries and wider doorways—are increasingly available.
Understanding zoning laws and building codes for prefabrication
Regulations in the United States depend on the home type and location. Manufactured homes must comply with the federal HUD Code and are often sited in zones that specifically allow them; local ordinances can set rules for placement, skirting, and permanent foundations. Modular and panelized homes are typically reviewed under state modular programs and must meet the IRC or IBC, then comply with local zoning rules covering setbacks, height, lot coverage, parking, and design standards. Some communities have architectural review or homeowners association requirements. Additional considerations include floodplain and coastal wind zones, snow loads, seismic design categories, fire sprinklers where required, energy code (IECC) compliance, and utility connection standards. Early coordination with local services such as planning departments, utility providers, and licensed contractors in your area helps prevent permitting delays.
Key advantages in today’s housing market
Prefab’s main benefits include schedule certainty, fewer weather disruptions, and tighter quality control. Material use can be optimized in a factory, helping reduce waste. Energy performance packages can improve comfort and lower operating costs over time. Because much of the work is standardized, pricing can be more transparent than bespoke site-built projects, though site conditions still matter. Potential challenges include transport logistics, crane staging, and local perceptions or rules about manufactured housing. Financing and appraisal are common but may follow different documentation paths than conventional custom builds; early engagement with lenders and insurers experienced in factory-built housing is useful.
Real-world pricing and provider comparison
Total project cost depends on location, design complexity, site work, and finishes. The figures below are broad estimates for the home and typical installation on a permanent foundation, excluding land, major site improvements, and extraordinary utility or access costs.
| Product/Service | Provider | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|
| Manufactured home (single/multi-section) | Clayton Homes | About $80–$140 per sq ft installed (excludes land and extensive site work) |
| Manufactured or modular offerings | Champion Home Builders | About $90–$160 per sq ft for manufactured; $150–$250 per sq ft for modular, installed |
| Manufactured homes | Cavco Industries | About $80–$140 per sq ft installed (scope varies by market) |
| Modular catalog homes | Connect Homes | Roughly $300–$420 per sq ft all-in before land, location-dependent |
| Modular custom and high-performance | Plant Prefab | Approximately $275–$500 per sq ft all-in before land, varies by design and region |
| Modular custom builds | Method Homes | Approximately $275–$450 per sq ft all-in before land and major site work |
| Panelized round and traditional models | Deltec Homes | Often $200–$350 per sq ft for total project costs before land, region dependent |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Conclusion: Prefabrication aligns factory precision with field assembly to deliver durable, code-compliant homes on compressed timelines. For many buyers, the approach offers clear benefits in predictability, quality control, and energy performance. With proper due diligence on zoning, codes, site conditions, financing, and provider capabilities, prefabricated housing can be a practical path to a well-built home in the United States.