Medical Assistant Training Programs Available in the US
Medical assistant training programs across the United States offer practical, hands-on experience for those interested in joining the healthcare field. Learn where to find training near you, what to expect from the courses, and how this path can lead to a stable medical career.
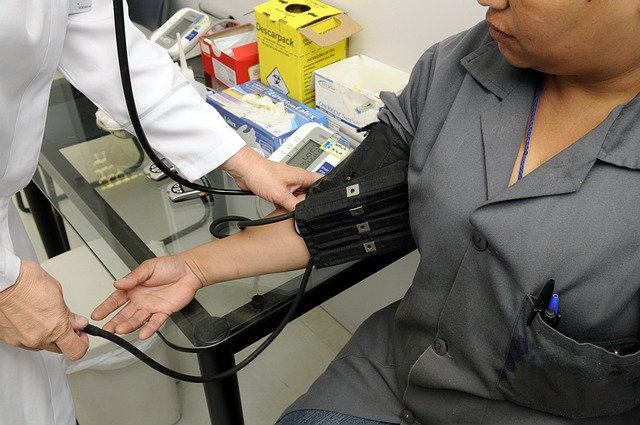
What Does a Medical Assistant Do on a Daily Basis?
Medical assistants serve as versatile healthcare professionals who handle both clinical and administrative responsibilities. On the clinical side, they take patient vital signs, prepare examination rooms, assist physicians during examinations, administer medications under supervision, perform basic laboratory tests, and collect biological specimens. Administratively, medical assistants schedule appointments, manage electronic health records, handle insurance forms, and coordinate patient communication. Many also serve as the first point of contact for patients, greeting them and gathering preliminary information about their health concerns. The role varies somewhat depending on the healthcare setting, with medical assistants in specialized practices often performing duties specific to that medical field.
What Topics and Skills Are Covered in Training Programs?
Medical assistant training programs provide comprehensive education covering both clinical and administrative aspects of the profession. Clinical instruction typically includes anatomy and physiology, medical terminology, pharmacology, laboratory procedures, clinical procedures, diagnostic testing, first aid, and CPR certification. Administrative education focuses on medical office procedures, healthcare documentation, insurance processing, electronic health records management, medical coding, and patient scheduling systems. Many programs also incorporate professional development topics such as healthcare ethics, patient confidentiality laws, communication skills, and cultural competence. Most importantly, accredited programs include hands-on laboratory practice where students can apply their knowledge in simulated healthcare environments before progressing to real-world clinical externships.
How Long Does It Take to Complete Medical Assistant Training?
The timeline for completing medical assistant training varies depending on the credential pursued. Certificate or diploma programs typically take 9-12 months to complete when attending full-time. Associate degree programs in medical assisting generally require two years of study. Part-time options exist for both pathways, though they extend the completion timeline accordingly. Most programs conclude with a required externship component lasting 4-8 weeks, providing real-world experience in actual healthcare settings. Accelerated programs are available at some institutions, allowing students to complete their training in as little as 6-8 months, though these often require more intensive study schedules. The certification examination process following program completion typically takes an additional 2-4 weeks.
Where Can You Find Accredited Medical Assistant Training Near You?
Accredited medical assistant training programs are available through various educational institutions across the country. Community colleges typically offer both certificate and associate degree options at competitive tuition rates, often with flexible scheduling. Technical and vocational schools specialize in career-focused training with concentrated medical assistant programs. Some hospitals and healthcare systems provide employer-sponsored training programs, sometimes with guaranteed employment opportunities upon completion. Online medical assistant programs with hands-on components are increasingly available, though these still require in-person clinical experiences arranged near your location.
To find accredited programs in your area, the Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs (CAAHEP) and the Accrediting Bureau of Health Education Schools (ABHES) maintain searchable databases of approved programs. Accreditation ensures that the program meets established educational standards and that graduates will be eligible for professional certification examinations.
What Are the Costs Associated with Medical Assistant Training?
Medical assistant training programs vary significantly in cost based on the type of institution and credential pursued.
| Program Type | Typical Cost Range | Duration | Additional Expenses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Certificate/Diploma (Community College) | $2,500-$6,000 | 9-12 months | Textbooks, uniforms, supplies: $500-$1,000 |
| Certificate/Diploma (Technical School) | $6,000-$15,000 | 9-12 months | Certification exam: $125-$250 |
| Associate Degree | $10,000-$25,000 | 2 years | Background check/immunizations: $100-$300 |
| Online Programs | $4,000-$12,000 | 9-18 months | Technology fees: $200-$500 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Financial aid options are widely available for medical assistant training, including federal student aid (for accredited programs), workforce development grants, and healthcare employer tuition assistance programs. Many institutions offer payment plans to help manage costs without requiring full upfront payment.
What Career Opportunities Are Available After Completing Training?
Graduates of medical assistant training programs have diverse career opportunities across the healthcare industry. Traditional settings include physician offices, where medical assistants may work directly with family practitioners, internists, or pediatricians. Hospitals employ medical assistants in outpatient departments, emergency rooms, and specialized units. Outpatient care centers provide opportunities in same-day surgical centers and urgent care facilities. Specialty clinics in fields like cardiology, dermatology, orthopedics, and obstetrics/gynecology often seek medical assistants with specialized training or experience.
Career advancement possibilities include becoming a medical office manager, healthcare administrator, or specialized medical assistant in areas such as ophthalmology or podiatry. Some medical assistants pursue additional education to become registered nurses, physician assistants, or other advanced healthcare professionals. The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects employment of medical assistants to grow 16% from 2021 to 2031, much faster than the average for all occupations, indicating strong job prospects for program graduates.
Medical assistant certification, while not required in all states, significantly enhances employment opportunities and earning potential. Major certifications include the Certified Medical Assistant (CMA) from the American Association of Medical Assistants, the Registered Medical Assistant (RMA) from American Medical Technologists, and the National Certified Medical Assistant (NCMA) from the National Center for Competency Testing.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.




